Enterprise Services Planning is a new modular 5-day training curriculum for managing modern businesses involving lots of knowledge work and creative services. If your organization contains people who must think and make decisions for their living then Enterprise Services Planning is the management training framework that will transform your business. While ideally taken together as 5 days of intensive emersion, ESP training is offered in 4 modules.
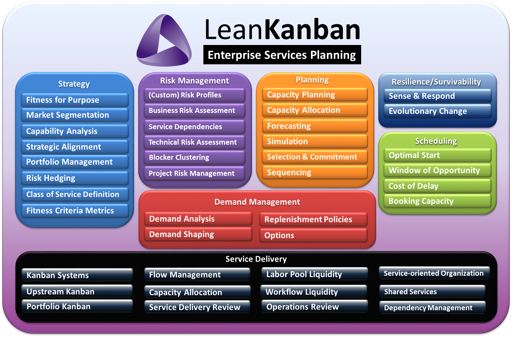
Map of the Enterprise Services Planning Framework
Enterprise Services Planning Module 2: Enterprise Services
Training class for up to 24 attendees
Duration: 1 day
Pre-requisites: Recommended KMP (Kanban Management Professional) or knowledge and experience of using kanban systems for services delivery. Basic understanding of market payoff from Cost of Delay section of Module 1
Foundation level understanding of Kanban systems is included as revision for attendees who don’t meet the pre-requisites
Target Audience
“I am a product manager. I’d wonder if we can use Kanban to manage development of ideas and requirements.”
“I am a product manager and I’d like to work more effectively with our delivery partners.”
“I am a service delivery manager and I’d like to know how to facilitate commitment meetings and replenish our kanban system.”
“I am a project manager and I want to know how to make and communicate plans when we are using Kanban to manage our delivery”
“I am a function manager and I want to understand how we can improve our delivery performance, shorten lead times and improve predictability”
“I am a process engineer and coach and I want to know how to advise our delivery organization on process improvement”
Curriculum
Day 3 – Options, Commitment & Delivery
- Posit Science case study – a bit of everything in this one, we also use it in coaching masterclasses
- Seeing Services – examples of how to put the Kanban Lens into action
- Understanding Kanban Systems
- mostly revision from Foundation training
- understanding commitment
- Little’s Law
- definition of Service Delivery Agility
- Options
- understanding real options
- understanding the value of options under various forms of uncertainty
- understanding how to balance option development with committed delivery based on uncertainty and risk
- Upstream Kanban
- embedded options
- governance framework for option development versus committed delivery
- minimum & maximum WIP limits
- discard rates in relation to uncertainty in the business domain
- defining organizational boundaries & commitment points
- Replenishment & Commitment
- replenishment meetings
- synchronous vs asynchronous commitment
- Understanding Lead Time
- histograms and distribution curves
- flow efficiency and its implications
- identifying sources of delay
- Chance versus Assignable Cause variation
- recognizing the type of variation
- understanding how to cope with chance cause variation by redefining the system in operation through policy changes
- understanding assignable cause variation and its relationship with event-driven risk
- learning the dynamics that left or right shift a lead time distribution or trim the tail on the distribution
Learning objectives
Observing STATIK (Systems Thinking Approach to Implementing Kanban) in action with Posit Science. Understanding risk profiling, asynchronous commitment and evolutionary change at Posit Science
Learning how to see services in an existing organization that can be improved with Kanban. Understanding that several services can be aggregated onto one kanban board and serviced by one team, or department.
Understanding fundamentals of kanban system mechanics at an advanced level including symmetrical versus asymmetrical commitment, Little’s Law, and how to define service delivery agility
Understand real option theory and learn to recognize the value of options under different conditions of uncertainty
Understand upstream Kanban, embedded options, minimum & maximum WIP limits, and the relationship to real option theory
Learn how to define a commitment point and organizational boundary based on uncertainty and risk assessment of the business domain
Learn to read and use lead time histograms and distribution curves. Understand the relationship of lead time distribution to Little’s Law
Understand the definition of flow efficiency and the implications of low flow efficiency environments and the system dynamics that affect lead time
Learn to identify typical sources of delay
Learn the difference between chance and assignable cause variation and how to manage them appropriately
Learn the management levers that can be pulled to left or right shift a lead time distribution curve or trim the tail from the curve
Understand how to use lead time distribution curves to communicate probability of delivery times and indicate predictability of delivery.
Who should attend?
Portfolio and program managers, project managers, service delivery managers, risk managers, those responsible for corporate governance, product managers, function/line managers or team leads, management trainers, management coaches, individual contributors working in creative or knowledge work service delivery or project environment, anyone responsible for service delivery to customers, anyone wishing to learn how to scale Kanban implementations beyond a single team or a single service workflow.
Applicability
This class is ideally suited to a single corporate for private delivery on premises. Typical scope should be a medium-sized entity or a product or business unit of a larger entity. The class is most suitable for the private sector but is adaptable to public sector environments.
Sales
Enterprise Services Planning classes are currently offered exclusively through David J. Anderson & Associates, Inc.
For open registration classes please consult our training listings http://anderson.leankanban.com/events If you don’t see a class listing near you please contact us sales@kanban.university
For private classes please email sales@kanban.university